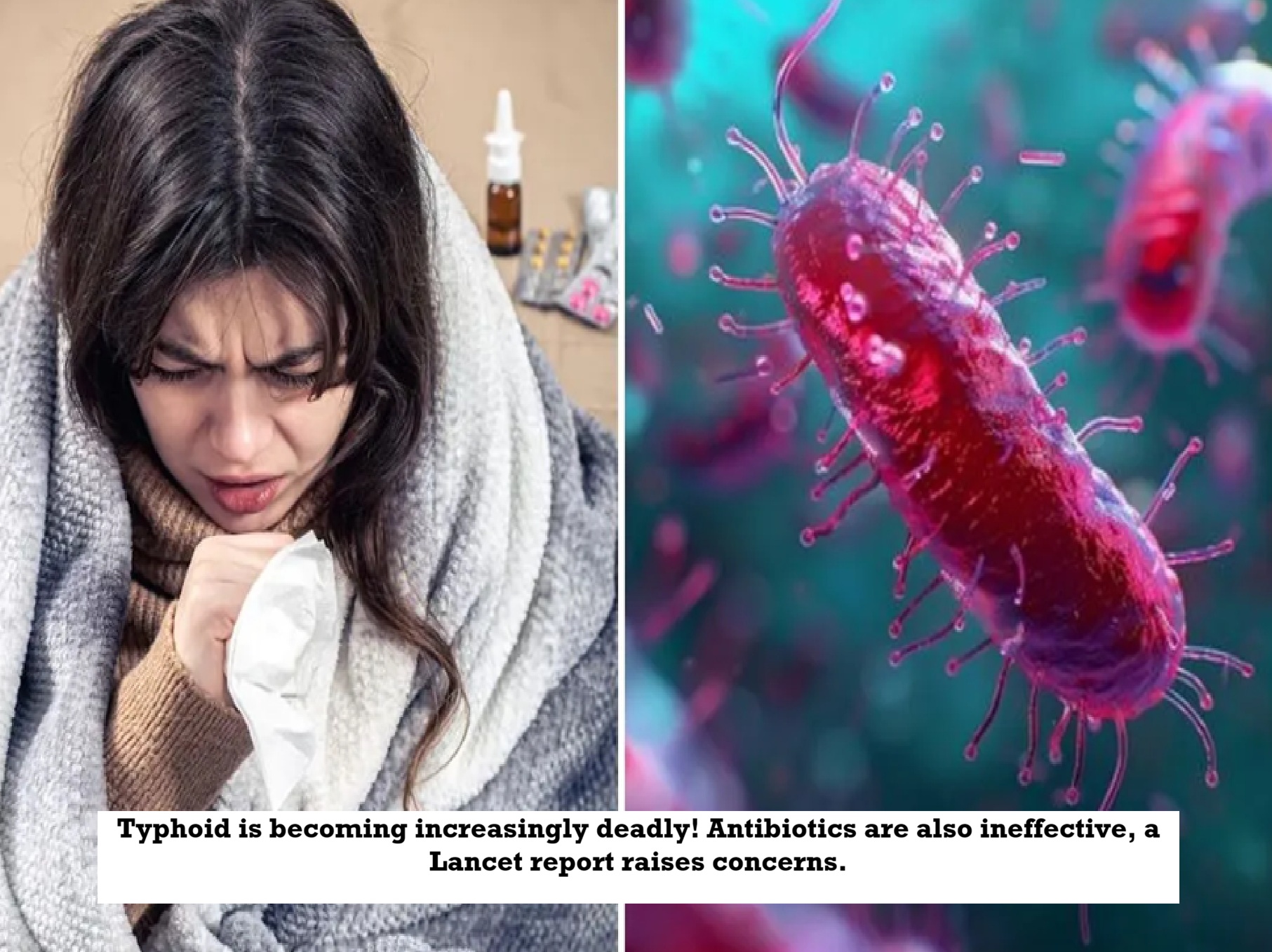
News Topical, Digital Desk : Typhoid is becoming more deadly in the country. This is because the bacteria responsible for it have developed resistance to the antibiotics cephalosporin and azithromycin. Antibiotics are not working and a large number of patients have to be hospitalized. According to a recent report by The Lancet, out of 7.3 lakh hospitalized cases of typhoid across the country in 2023, 6 lakh cases were due to fluoroquinolone-resistance. This is the ability of bacteria by which they neutralize the effect of antibiotics.
Fluoroquinolone resistance is a major cause of death
According to the report, fluoroquinolone resistance is a major cause of typhoid-related hospitalizations and deaths, especially among children under five years of age, and resistance to fluoroquinolones remained at a consistently high level (over 60 percent) in the most affected states of the country. It continued to rise from 1989 to 2024, reaching 94 percent in 2017.
More cases in Delhi, Maharashtra
Researchers from the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine and the Christian Medical College in Vellore, India, found that Delhi, Maharashtra, and Karnataka had the highest rates of fluoroquinolone-resistant cases and deaths. Therefore, Delhi, Maharashtra, and Karnataka have been selected as priority states for the introduction of the typhoid conjugate vaccine, a single-dose vaccine that provides long-term protection.
Medication monitoring is necessary
The team said that relying solely on routine vaccination programs, which administer typhoid conjugate vaccine to children as young as nine months old, cannot immediately control typhoid in India . It could take decades to reach older adults, who are most vulnerable to the disease. To combat this, measures to control antimicrobial resistance (AMR) are essential, including antimicrobial stewardship programs, infection prevention and control strategies, and improved monitoring of both AMR and antimicrobial drug use.
Symptoms of typhoid fever
Typhoid fever is a bacterial infection spread through contaminated food and water. Symptoms begin one to three weeks after infection, including high fever, headache, abdominal pain, and fatigue. It is treated with antibiotics and close attention.
--Advertisement--

 Share
Share



