Thrombosis is a disease that affects millions of people worldwide, but most people still don't know about it. Still, the number of reported cases and the potential harm it can cause mean we need to talk about it and learn about it. It's a silent killer.
What is thrombosis?
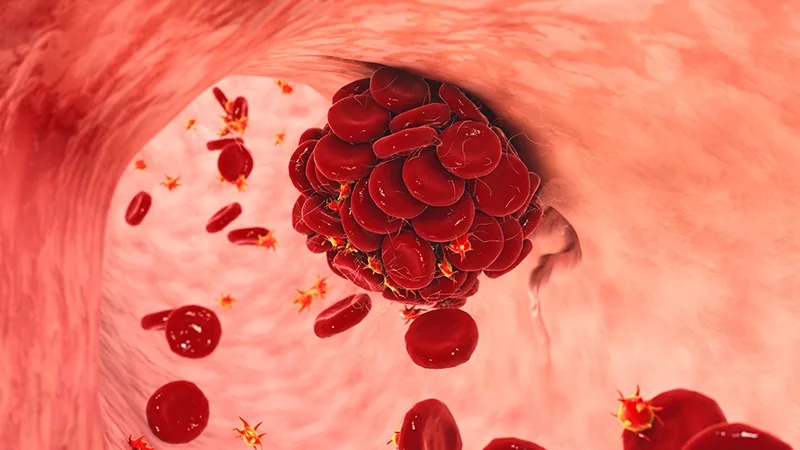
Medical terms define thrombosis as a process in which a blood clot forms within a blood vessel. These clots can occur within the arterial or venous system. And they can be fatal. When a blood clot forms, it blocks blood flow in its normal path, seriously affecting the patient, which can lead to a heart attack, stroke, or pulmonary embolism.
Causes of Thrombosis
There are several risk factors that increase the likelihood of thrombosis. These include sedentary lifestyle, obesity, smoking, pregnancy, genetics and age.
Symptoms of thrombosis
Swelling in the affected area, i.e. in your leg or arm.
Redness or discoloration of the skin appears in the affected area.
Pain or tenderness in the affected area.
The area feels warm.
In case of pulmonary embolism, you may experience shortness of breath and chest pain.
Types of thrombosis
Arterial thrombosis: This is a condition of thrombosis in which a blood clot forms in an artery. Arteries carry oxygen and blood from the heart to other parts of the body. This can lead to serious conditions like stroke or heart attack.
Venous thrombosis: Venous thrombosis occurs when a blood clot forms in a vein. The role of the vein is to carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart. This causes deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE).
Treatment of thrombosis
Anticoagulants: These medications will prevent the formation of further clots and allow your body to dissolve clots that have already formed.
Thrombolytics: In some cases, medications are given to treat clots that have already formed.
Surgery: In severe cases, the clot can be removed or the narrowed blood vessel can be opened by surgical intervention.
Prevention of thrombosis
Exercise: Regular exercise improves blood flow and prevents the formation of blood clots in the veins.
Quitting smoking: Quitting smoking can improve the health of your blood vessels, ensuring a lower chance of thrombosis in healthy blood vessels.
Maintain a healthy weight: Maintaining a healthy weight will relieve most of the pressure on your veins and reduce the chances of blood clots.
Hydration: Drinking enough water helps keep your blood fluid; this prevents your blood from becoming too thick, which makes it less likely to clot.
Move around: When you sit for several hours, you need to get up and move around to prevent blood from pooling in your legs.
Read More: Do you keep the lid open when flushing? This American research will reveal your eyes.
--Advertisement--

 Share
Share



